Importance of Socialization in School
Socialization is an essential process that plays a critical role in a child's development and growth. Schools are often considered the primary agents of socialization, providing a structured environment where children learn important social skills, values, and norms that are necessary for successful integration into society.
Socialization helps children develop their personalities and shapes their behavior, attitudes, and beliefs. It enables them to learn how to interact with others, form relationships, and understand their roles within the community.
Through socialization, children learn the rules of society, including norms, values, customs, and traditions, and acquire the necessary skills to function effectively in the world around them.
Socialization plays a pivotal role in shaping students' lives, especially in educational settings. As they grow and develop, students interact with various individuals and groups, learning valuable skills that will guide them throughout their lives.
In this blog, we will explore the importance of socialization in education, focusing on how schools play a critical role in socializing students and preparing them for the challenges of the world.
Why Is Socialization Important?
Socialization is not just about making friends or interacting with peers; it is a fundamental process that helps students learn the norms, values, and behaviors crucial for their success in society. By engaging with others in educational settings, students develop key life skills such as empathy, communication, and problem-solving.
Moreover, socialization in schools is essential for the emotional, cognitive, and social development of students, helping them adjust to the expectations of the world around them. It nurtures emotional intelligence, resilience, and cooperation, which are vital traits for navigating both personal and professional environments.
What is Socialization?
Socialization is a process through which individuals learn and adapt to the norms, values, customs, and ideologies of their culture or society. It is a continuous process that begins at birth and continues throughout life, shaping a person's beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors.
The primary goal of socialization is to prepare individuals for participation in social, economic, and political life. Through this process, individuals learn how to communicate, interact with others, and understand their roles and responsibilities within society.
What are the Agents of Socialization?
Agents of socialization are the individuals, groups, and institutions that influence a person's social development and help them learn the norms and values of their culture.
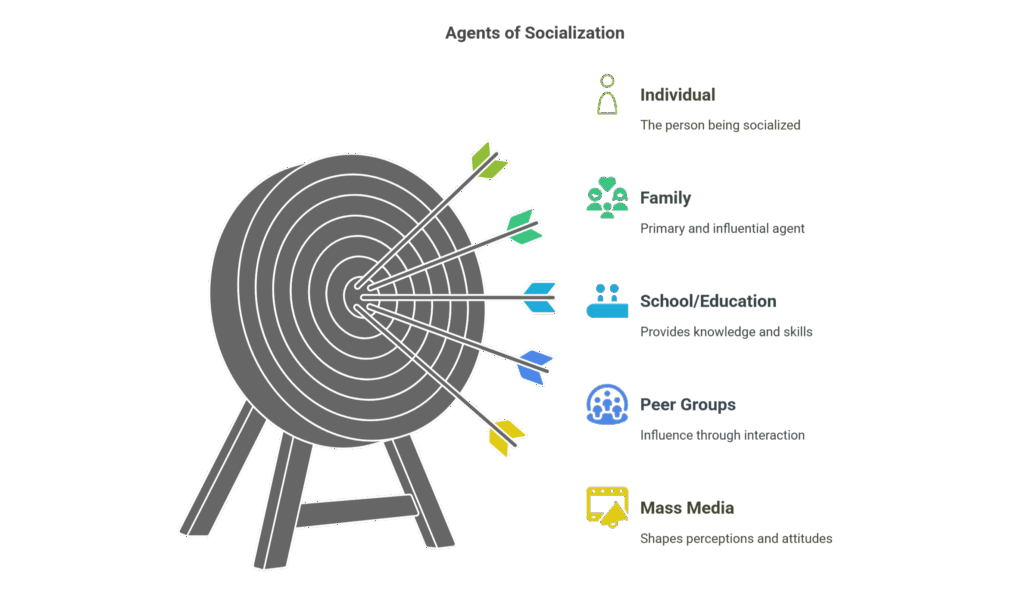
The main agents of socialization include:
- Family
- School/Education
- Peer Groups
- Mass Media
- Religion
Each agent of socialization plays a unique role in shaping a person's beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. For example, the family is often the first and most influential agent of socialization, while schools play a critical role in teaching children the knowledge and skills necessary for success in society.
How Schools Facilitate Socialization
Schools are powerful agents of socialization. They serve as a platform where children interact with their peers and teachers, providing them with the opportunity to develop strong social skills.
The role of school in socialization goes beyond academics. Schools provide a safe space for children to express themselves, form friendships, and learn how to work collaboratively with others.
Teachers and school staff play an essential part in guiding this process. They encourage students to participate in group activities, communicate effectively, and constructively resolve conflicts.
Schools also expose students to diverse social environments, which can help them develop tolerance and understanding of different cultures, backgrounds, and perspectives.
How Schools Promote Socialization
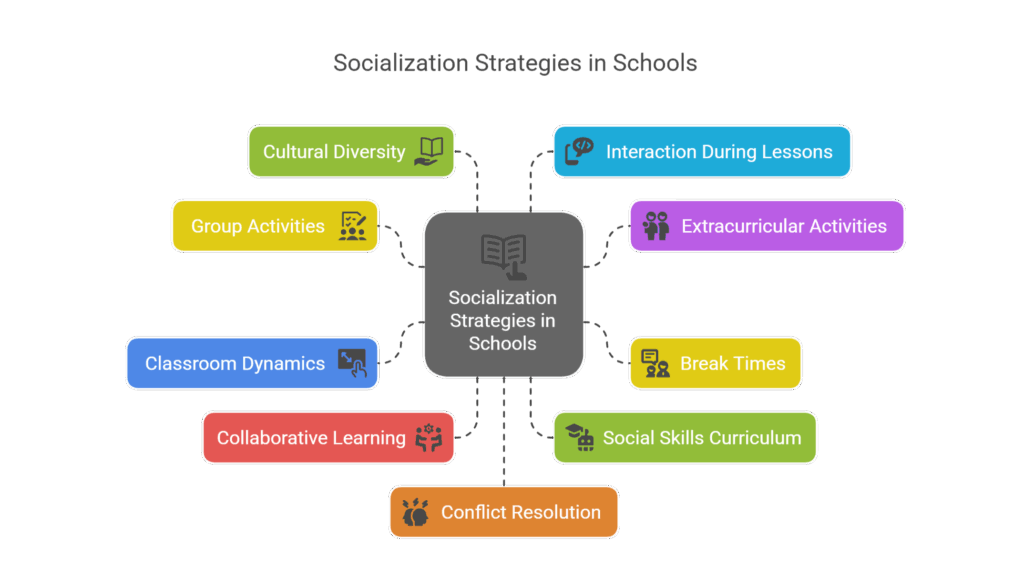
The school plays a vital role in promoting socialization among children by providing a structured environment where they can learn and develop important social skills. Some of how schools promote socialization include:
- Conducting Group Activities: Group projects, presentations, and workshops encourage teamwork, leadership, cooperation, and problem-solving skills.
- Participating in Extracurricular Activities: Clubs, sports, and arts groups connect students with peers who share their passions, boosting self-confidence and nurturing lifelong friendships.
- Socializing During Break Times: Recess and lunch periods offer informal spaces to build friendships, practice negotiation, and naturally resolve minor conflicts.
- Changing Classroom Dynamics: Open discussions, debates, and personal storytelling foster active listening, empathy, and respect for diverse viewpoints.
- Creating Collaborative Learning Environments: Collaborative classrooms allow students from diverse backgrounds and skill levels to learn from one another, promoting mentorship and patience.
- Implementing a Social Skills Curriculum: Some schools formally teach emotional intelligence, communication, and conflict resolution through special classes and activities.
- Teaching Cultural Diversity: Exposure to different cultures through festivals and projects encourages global awareness and acceptance.
- Encouraging Interaction During Lessons: Academic teamwork and peer discussions promote respectful communication and critical thinking.
- Teaching Conflict Resolution: Students learn peaceful problem-solving techniques through teacher-led mediation.
- Providing Proper Teacher Guidance: Supportive teachers recognize individual strengths and encourage leadership, empathy, and collaboration.
- Lessons on Acceptance and Rejection: Through real-world consequences, children learn which behaviors earn social acceptance and which do not.
- Following Traditions and Celebrating Festivals: Events like Diwali, Eid, and Christmas teach cultural respect and community building.
The Role of Teachers in Socialization
Teachers are central figures in the socialization process. They not only impart knowledge but also model appropriate behaviors and teach students the social norms they need to succeed.
The role of the teacher in socialization involves setting expectations for how students should behave in social situations, fostering positive relationships, and creating an inclusive environment where every student feels valued.
By encouraging cooperation, empathy, and respect among students, teachers help to create a positive learning environment that supports social development.
The Impact of Socialization on Education
The impact of socialization on education cannot be overstated. A well-socialized student is more likely to thrive in a classroom setting, both academically and socially.
Socialization helps students feel more comfortable expressing their ideas and opinions, leading to better classroom participation and academic success. It also fosters emotional intelligence, which is crucial for building healthy relationships and navigating challenges throughout life.
Furthermore, students who are socialized effectively in school are better equipped to transition into adulthood.
They gain a sense of responsibility, develop leadership skills, and learn how to work in teams, all of which are highly valued in the professional world.
The Role of Socialization in Shaping Identity
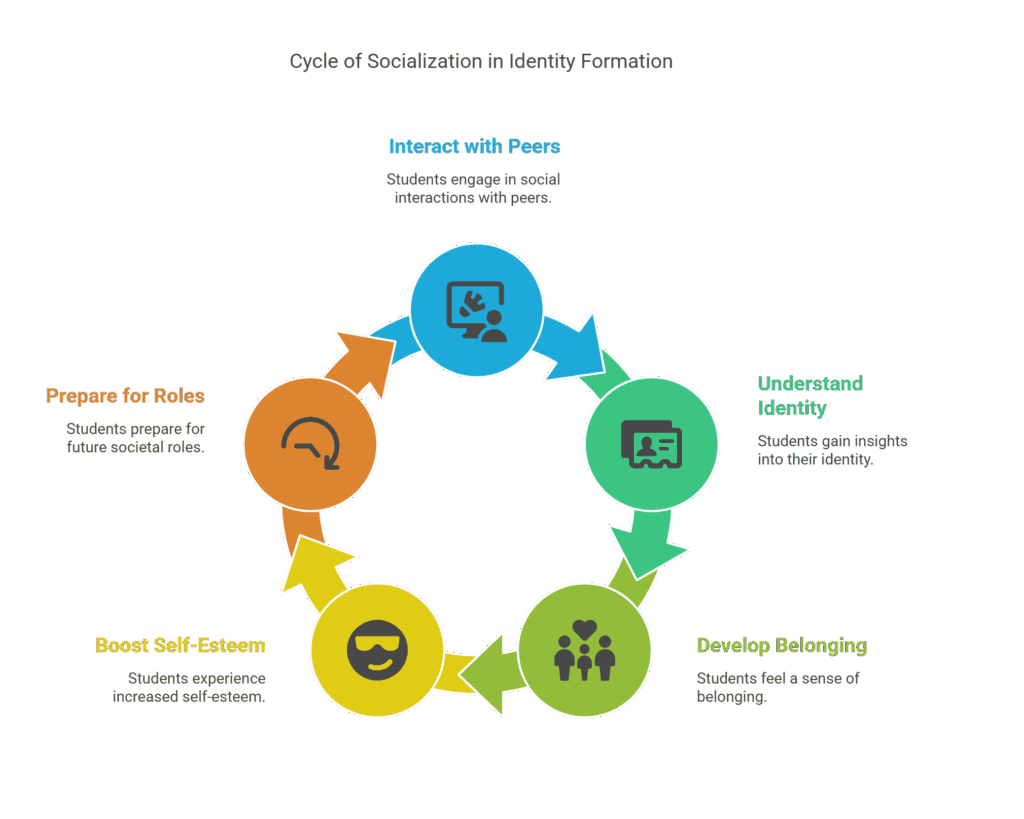
Socialization also plays a significant role in shaping a student’s identity.
As they interact with peers and teachers, students begin to understand who they are and how they fit into society. School socialization helps students develop a sense of belonging, which can boost their self-esteem and confidence.
This process is essential in preparing students to take on roles in society, whether it's as a student, a friend, or a future professional.
How Socialization in School Impacts Children's Behavior in Society
The role of school in socialization plays a crucial part in shaping a child's behavior in society. By teaching children important social skills, values, and norms, schools help prepare them for the challenges of adult life.
Through socialization, children learn how to interact with others, form relationships, and understand their roles within the community. They also learn how to communicate effectively, resolve conflicts, and work collaboratively with others. These skills are essential for success in the modern world and are highly valued by employers and society as a whole.
Moreover, socialization in school helps children develop a sense of identity and belonging. By participating in group activities and forming friendships, children learn to appreciate diversity and respect different perspectives. They also learn to value teamwork, cooperation, and collaboration, which are essential for building strong and inclusive communities.
The Broader Impact of School Socialization
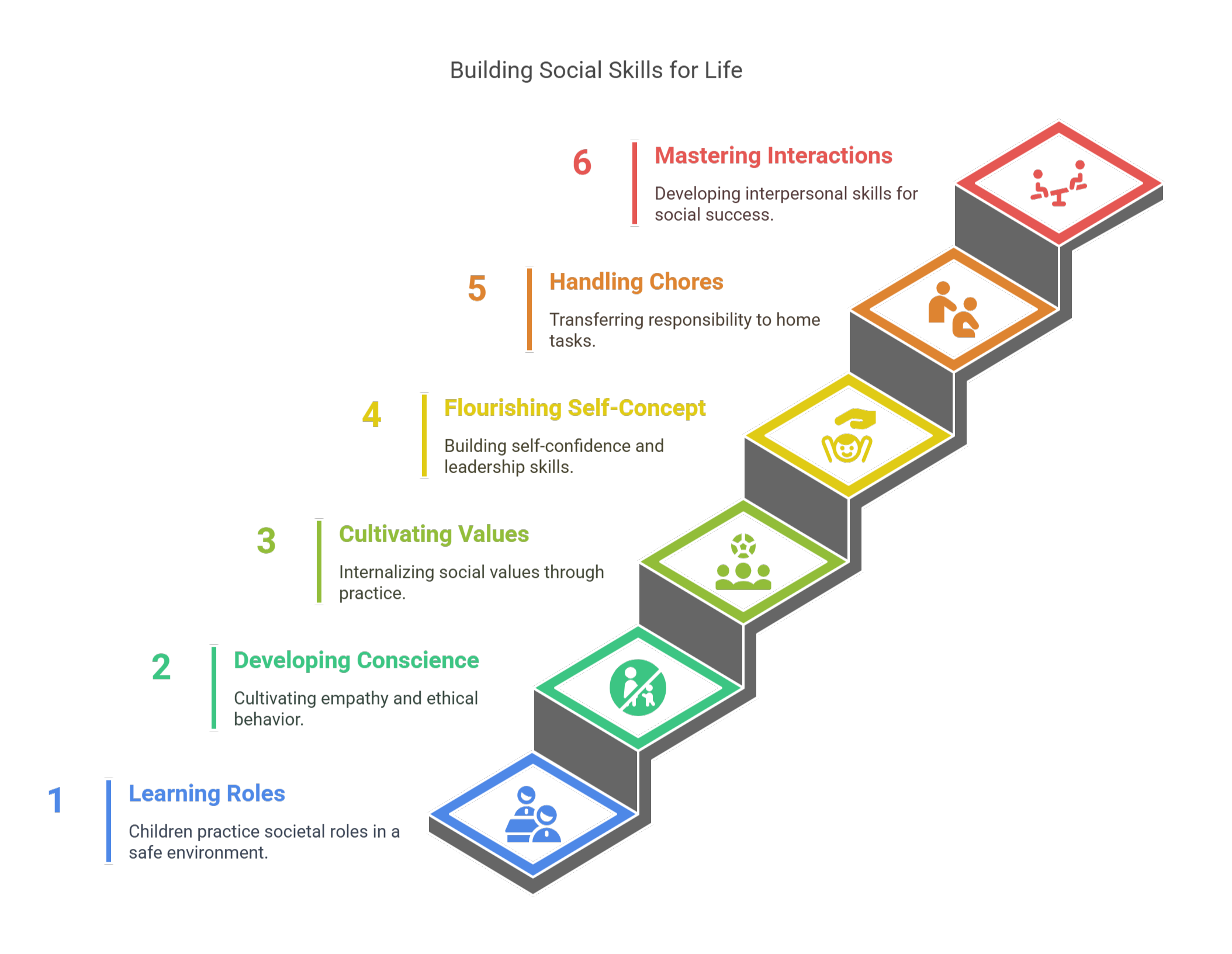
Socialization at school has a profound impact on children’s behavior in the broader world. The lessons learned in the classroom ripple outward, shaping values, interactions, and personal growth in powerful ways:
- Learning Societal Roles:
Children practice different roles—such as friend, teammate, and leader—within the safe environment of school, preparing them for the responsibilities they will encounter in society. - Developing a Conscience:
Through daily interactions and adherence to formal school rules, children cultivate empathy, a sense of responsibility, and ethical behavior, forming the foundation for moral decision-making in adulthood. - Cultivating Values and Implementing Skills:
Social values like respect, communication, and teamwork become second nature through repeated practice, equipping children to function effectively in diverse social and professional settings. - Flourishing Self-Concept:
Positive recognition and encouragement at school play a crucial role in building children's self-confidence, enabling them to grow into capable adults who are ready to lead and inspire others. - Handling Household Chores:
Responsibility learned through tasks like classroom jobs often transfers into the home environment, fostering independence, collaboration, and a strong work ethic. - Mastering Social Interactions:
From negotiating playground conflicts to collaborating on group projects, students develop critical interpersonal skills that are essential for thriving in society.
While family, media, and community also contribute to a child's development, schools remain irreplaceable in shaping responsible, socially adept future citizens. School's structured social environment prepares children academically and molds them into empathetic, ethical, and empowered individuals who can positively influence the world around them.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, socialization in school plays a critical role in shaping a child's development and preparing them for success in society.
By providing a structured environment where children can learn important social skills, values, and norms, schools help to promote positive social development and foster a sense of identity and belonging.
By working together, teachers, parents, and communities can help create a supportive and inclusive environment that supports the social development of all children, ensuring that they are well-prepared to thrive in the modern world.
FAQs On Socialization
1. How does a school function as a socialization agency?
Schools aren’t just about textbooks—they act as mini-societies where students learn norms, values, and roles by doing and observing others. Émile Durkheim even called schools “socialization agencies” because they teach kids to cooperate, follow rules, and prepare for civic and economic life. In practice, this happens through both manifest functions, like teaching respect for authority, and latent ones, such as building peer networks that can last a lifetime.
2. Why is socialization important for students’ academic and emotional development?
Fundamentally, socialization in schools underpins both learning and well-being. Research shows that children exposed to supportive social environments often outperform their peers academically and cope better with stress and setbacks. When kids feel heard and valued, they build self-esteem and emotional resilience, helping them navigate challenges inside and outside the classroom.
3. What specific activities help socialization in schools?
Oh, there’s a ton—group projects, peer tutoring, and workshop-style lessons all prime the pump for teamwork and empathy. Recess and lunch periods may feel unstructured, but these informal breaks are where children practice negotiation, inclusion, and casual conversation. Some schools even run role-playing scenarios to teach conflict resolution and emotional intelligence as part of a formal social-skills curriculum.
4. What roles do teachers and peers play in school-based socialization?
Teachers often serve as behavior models, mediators, and confidence coaches, encouraging quieter students to speak up or guiding classes through respectful debates. Their subtle cues—like acknowledging fair play or celebrating kindness—shape the classroom culture more than we might realize. Peers, on the other hand, drive norm formation: through group work or even playground disputes, students negotiate roles, test boundaries, and learn empathy firsthand.
5. Why is teaching cultural diversity critical for socialization in schools?
Exposure to different cultures and perspectives in the classroom builds global awareness and reduces bias from a young age. Celebrating festivals or integrating multicultural content helps kids see diversity as an asset rather than something to fear. Plus, inclusive group tasks teach students to value varied viewpoints—an essential skill in our interconnected world.